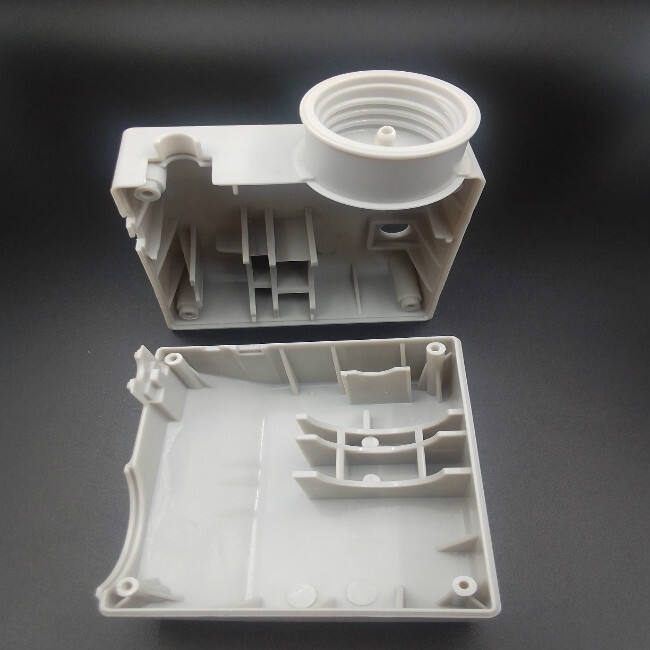
Introduction to Plastic Molding Processes
The Role of Plastic Molding in Modern Manufacturing
Plastic molding is a cornerstone of contemporary manufacturing, facilitating the mass production of intricate shapes and designs. This manufacturing process, crucial for cost-effective and scalable production, caters to diverse sectors by reducing waste and enhancing efficiency. The versatility of plastic materials is profound, enabling their application in consumer products, automotive components, and industrial equipment. This adaptability not only broadens the scope of applications but also supports innovation across industries, highlighting plastic molding's indispensable role in modern manufacturing.
Why Understanding Different Processes Matters
Understanding the distinct characteristics of each plastic molding process is essential for optimizing production efficiency and enhancing product quality. Different processes affect product design, material selection, and production workflows significantly. By acknowledging these differences, manufacturers can select appropriate processes for specific applications, ensuring cost-effective, high-quality outcomes. Each method offers unique benefits and limitations, impacting factors like costs and final product quality. Making informed decisions in this regard can lead to improved production outcomes and align with business goals, ultimately driving success across industrial applications.
Injection Molding: Precision and Versatility
Process Overview: Melting and Injecting Polymers
Injection molding involves melting raw plastic pellets and injecting them into a predetermined mold, where they cool and solidify into the final product. This precise process enables manufacturers to create complex parts with tight tolerances, offering high precision and repeatability. Industries benefit significantly from the rapid production cycles and reduced material waste that injection molding provides, making it an ideal choice for large-scale manufacturing. By understanding the nuances of injection molding processes, businesses can optimize their production strategies and improve their output quality.
Key Applications: Automotive, Medical, and Consumer Goods
Injection molding plays a crucial role across various industries, notably in automotive, medical, and consumer goods. In the automotive sector, it is indispensable for producing durable and precise parts like dashboards and bumpers. The medical field relies on injection molding to fabricate sterile components such as syringes and surgical tools with high quality and precision. Additionally, consumer goods—including toys and household items—frequently utilize injection molding for its cost-effectiveness and reliability, ensuring consistent mass production of complex designs across multiple fields.
Advantages and Limitations
The principal advantages of injection molding include high-speed production, uniformity in product quality, and reduced labor costs due to automation. However, the process does come with limitations, primarily the high initial tooling costs and the lack of flexibility for design changes once a mold is finalized. Balancing these factors is crucial for manufacturers to determine the feasibility and cost-effectiveness of using this process for specific projects. Making informed decisions regarding these variables can significantly affect a company's production efficiency and product quality, aligning with broader business goals.
Blow Molding: Crafting Hollow Forms
How Air Shapes Plastic into Containers
Blow molding is a fascinating process that employs air pressure to shape melted plastic into hollow forms. The technique begins with raw plastic being melted to create a parison, which is essentially a molten tube. Air is then injected into the parison, causing it to expand and conform to the mold's shape. This process not only enables efficient manufacturing of hollow plastic products but also minimizes material use. It proves particularly advantageous for producing large quantities of complex shapes with thin walls, ensuring both speed and economy.
Applications: Bottles, Fuel Tanks, and Drums
Blow molding finds primary applications across various industries, notably in the production of bottles, fuel tanks, and industrial drums. Beverage bottles, made through blow molding, must adhere to strict safety standards to ensure consumer protection. In automotive manufacturing, blow molded fuel tanks are appreciated for their strength and lightweight properties, enhancing vehicle performance. Industrial drums created via blow molding are essential for securely transporting liquids, designed for durability and efficiency. These applications underscore blow molding's versatility in crafting crucial components with precision.
Material Compatibility and Efficiency
The blow molding process is highly compatible with a range of thermoplastic materials, such as polyethylene and polypropylene. This compatibility expands its usability, as these materials offer excellent strength and durability, vital for various applications. Additionally, blow molding is celebrated for its efficiency in material usage, significantly reducing waste and costs. Understanding the compatibility of materials with different blow molding processes is thus key to optimizing product performance, making it a popular choice among manufacturers seeking cost-effective solutions.
By exploring the nuances of blow molding, the intricate art of crafting hollow forms becomes evident, showcasing its significance in modern manufacturing.
Compression Molding: Strength and Durability
Heat, Pressure, and Curing
Compression molding relies on the dual application of heat and pressure to mold materials, predominantly using thermosetting plastics that undergo a vital curing phase. This molding process is instrumental in producing components that exhibit enhanced strength and durability, making it ideal for applications requiring high-stress endurance. Successful production via compression molding is deeply rooted in understanding the appropriate curing times and temperatures as they are critical to achieving optimal results. This mastery ensures the integrity and performance of the final product, tailored for rigorous applications.
Common Uses: Electrical Components and Industrial Parts
The utility of compression molding spans several critical industries, notably in the manufacture of electrical components and industrial parts. For electrical applications, components made from this molding process play a crucial role in wiring and circuit boards, valued for their resilience and reliability. In the industrial sector, parts such as gears and seals benefit significantly from the strength achieved through compression molding, rendering them suitable for high-demand applications. This widespread use underscores the process's significance in the manufacturing landscape, playing a pivotal role in producing heavy-duty items that require robust performance.
Benefits for High-Strength Products
Compression molding stands out for its capability to produce high-strength products highly valued in sectors like automotive and aerospace. The process achieves a density in the materials that is essential for applications where optimal strength-to-weight ratios are crucial. By leveraging the compression molding technique, manufacturers can craft items designed to endure rigorous conditions, providing a competitive edge in developing components that must withstand intense and prolonged mechanical stress. This capability not only enhances product performance but also offers economic advantages in the long-term reliability and durability of the products created.
Rotational Molding: Large and Hollow Components
The Role of Rotation in Uniform Wall Thickness
Rotational molding is a unique process that creates even wall thickness by rotating molds around two axes while heating them. This rotation allows the plastic material to distribute evenly across the mold, resulting in durable and consistent hollow parts. Such uniform wall thickness is crucial for products that must withstand stress without warping, ensuring superior durability and reliability. This consistency is particularly important for industries where high standards are a prerequisite, making rotational molding an invaluable technique.
Applications: Storage Tanks and Playground Equipment
Rotational molding is famously used to make large storage tanks and playground equipment, thanks to its ability to produce durable, seamless structures. Storage tanks benefit from this technique's capacity to create robust components that can handle significant stress and weathering, ensuring a long lifespan. Playground equipment produced through rotational molding provides safety and design versatility, enabling a wide range of playful configurations. The process's adaptability to large, hollow designs makes it indispensable across multiple sectors, from agriculture to leisure.
Sustainability and Waste Reduction
A significant advantage of rotational molding is its sustainability, which is achieved through efficient material usage and reduced scrap rates. This method often incorporates recyclable materials, minimizing environmental impact and fostering a more sustainable manufacturing process. Furthermore, rotational molding helps companies adhere to environmental regulations by optimizing material efficiency without compromising production effectiveness. Employing this approach not only benefits the environment but also enhances the company's reputation by aligning with eco-friendly practices.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is plastic molding?
Plastic molding is a manufacturing process used to create diverse products by shaping and forming plastics into predetermined designs.
Why are different plastic molding processes important?
Different processes offer unique benefits and limitations that affect production efficiency, design flexibility, and product quality, ensuring the best outcomes for specific applications.
Which industries benefit the most from injection molding?
Industries like automotive, medical, and consumer goods significantly benefit from injection molding due to its precision and suitability for mass production.
How does blow molding differ from other molding techniques?
Blow molding uses air pressure to shape melted plastic into hollow forms, making it ideal for producing items like bottles and fuel tanks.
Is rotational molding more sustainable than other methods?
Yes, rotational molding is recognized for its efficient material usage and reduced waste, often incorporating recyclable materials to minimize environmental impact.